Best EBUS-TBNA Treatment in Thane
- Treatments
- BronchoscopyBronchoscopy
- EBUS-TBNAEBUS-TBNA
- Transbronchial Lung BiopsyTransbronchial Lung Biopsy
- Semi-Rigid Medical ThoracoscopySemi-Rigid Medical Thoracoscopy
- ThoracentesisThoracentesis
- Intercostal Drain InsertionIntercostal Drain Insertion
- Pigtail Catheter InsertionPigtail Catheter Insertion
- PleurodesisPleurodesis
- Closed Pleural BiopsyClosed Pleural Biopsy
- USG & CT Guided Lung Mass BiopsyUSG & CT Guided Lung Mass Biopsy
- Sleep StudySleep Study
- Pulmonary Function TestingPulmonary Function Testing
- Post-COVID RehabilitationPost-COVID Rehabilitation
- Pulmonary Hypertension ClinicPulmonary Hypertension Clinic
- Smoking Cessation TherapySmoking Cessation Therapy
EBUS-TBNA
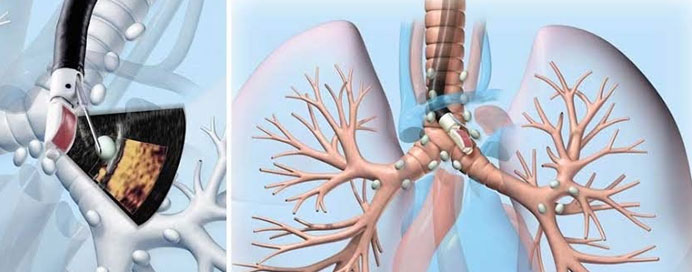
Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) is an advanced, minimally invasive procedure used to visualize and sample lymph nodes and masses located around the trachea and bronchi. Using a bronchoscope equipped with an ultrasound probe, doctors can accurately locate abnormal lymph nodes or growths and collect tissue samples without the need for surgical incisions. EBUS-TBNA is widely used for diagnosing lung cancer, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and other mediastinal diseases. It offers high accuracy, minimal discomfort, and quick recovery, making it a preferred alternative to more invasive surgical biopsies.
Why EBUS-TBNA Is Performed
- To diagnose enlarged or abnormal lymph nodes in the chest.
- To evaluate suspected lung cancer or confirm cancer staging.
- To diagnose conditions like tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, or lymphoma.
- To obtain tissue samples from areas not reachable by regular bronchoscopy.
- To avoid more invasive surgical procedures like mediastinoscopy.
How EBUS-TBNA Is Done
- The patient receives sedation or anesthesia for comfort.
- A bronchoscope with an ultrasound probe is inserted through the mouth.
- Ultrasound imaging identifies the exact lymph node or mass.
- A fine needle is passed through the airway wall to collect samples.
- The procedure typically takes 30–45 minutes with minimal recovery time.
Benefits of EBUS-TBNA
- High diagnostic accuracy for lung and mediastinal diseases.
- Minimally invasive with no surgical cuts or stitches.
- Allows real-time imaging for precise sampling.
- Reduces the need for more invasive surgeries and hospitalization.
- Quick recovery and minimal post-procedure discomfort.
