Best Interstitial Lung Disease Treatment in Thane
- Diseases
- AsthmaAsthma
- COPDCOPD
- Interstitial Lung DiseaseInterstitial Lung Disease
- PneumoniaPneumonia
- Sleep ApneaSleep Apnea
- Bronchitis & Chronic CoughBronchitis & Chronic Cough
- Pulmonary FibrosisPulmonary Fibrosis
- TuberculosisTuberculosis
- SarcoidosisSarcoidosis
- Lung Cancer EvaluationLung Cancer Evaluation
- Pleural EffusionPleural Effusion
- PneumothoraxPneumothorax
- Pulmonary EmbolismPulmonary Embolism
- ARDSARDS
- Allergic Lung DiseasesAllergic Lung Diseases
- Post-COVID Lung DiseasePost-COVID Lung Disease
- Occupational Lung DiseasesOccupational Lung Diseases
Interstitial Lung Disease
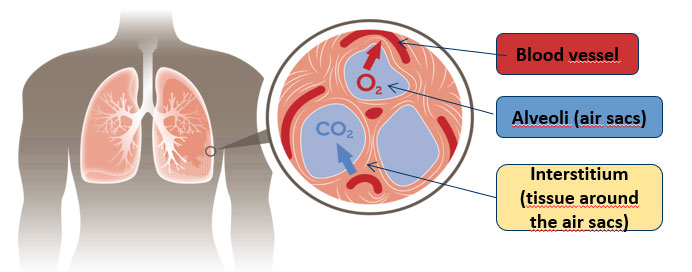
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) is a group of disorders that cause progressive scarring of the lung tissue, making the lungs stiff and less able to function properly. This leads to difficulty in breathing, reduced oxygen exchange, and fatigue. ILD can result from autoimmune conditions, environmental exposures, medications, infections, or sometimes have no identifiable cause (idiopathic). Early diagnosis and management are essential to slow progression and improve quality of life.
Causes & Risk Factors
- Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or scleroderma
- Long-term exposure to dust, asbestos, or silica
- Certain medications, including chemotherapy or antibiotics
- Chronic lung infections
- Idiopathic (unknown) causes
Symptoms & Diagnosis
- Gradual shortness of breath, especially on exertion
- Persistent dry cough
- Fatigue and weakness
- High-resolution CT scan (HRCT) to detect lung scarring
- Pulmonary function tests to measure lung capacity and airflow
