Best Pulmonary Embolism Treatment in Thane
- Diseases
- AsthmaAsthma
- COPDCOPD
- Interstitial Lung DiseaseInterstitial Lung Disease
- PneumoniaPneumonia
- Sleep ApneaSleep Apnea
- Bronchitis & Chronic CoughBronchitis & Chronic Cough
- Pulmonary FibrosisPulmonary Fibrosis
- TuberculosisTuberculosis
- SarcoidosisSarcoidosis
- Lung Cancer EvaluationLung Cancer Evaluation
- Pleural EffusionPleural Effusion
- PneumothoraxPneumothorax
- Pulmonary EmbolismPulmonary Embolism
- ARDSARDS
- Allergic Lung DiseasesAllergic Lung Diseases
- Post-COVID Lung DiseasePost-COVID Lung Disease
- Occupational Lung DiseasesOccupational Lung Diseases
Pulmonary Embolism
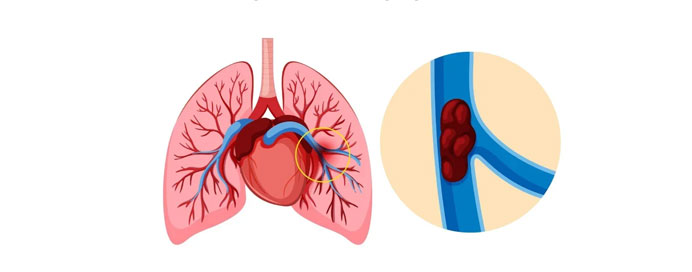
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition in which a blood clot, usually formed in the deep veins of the legs, travels to the lungs and blocks a pulmonary artery. This obstruction reduces oxygen supply, strains the heart, and can cause sudden breathlessness, chest pain, or collapse. Early diagnosis through imaging and prompt treatment with blood thinners or advanced interventions is essential to prevent complications and improve survival.
- Causes & Risk Factors: Deep vein thrombosis, prolonged immobility, surgery, trauma, obesity, pregnancy, cancer, smoking, and clotting disorders increase PE risk.
- Symptoms: Sudden shortness of breath, sharp chest pain, rapid heartbeat, coughing (sometimes with blood), dizziness, or fainting.
- Diagnosis: CT pulmonary angiography, D-dimer testing, Doppler ultrasound of legs, and ECG/echocardiography to assess heart strain.
- Treatment: Anticoagulants (blood thinners), thrombolytic therapy for severe cases, catheter-based clot removal, and supportive oxygen therapy.
- Prevention: Early mobilization after surgery, use of compression stockings, staying hydrated, avoiding prolonged sitting, and prophylactic anticoagulants in high-risk patients.
